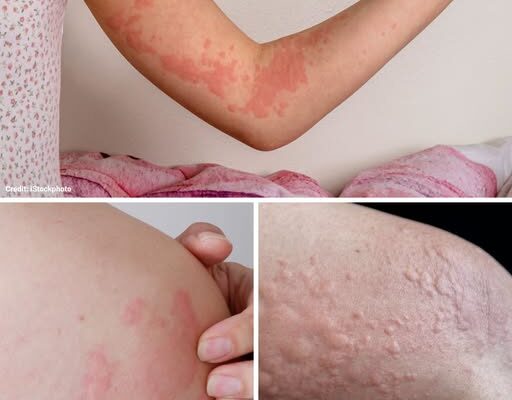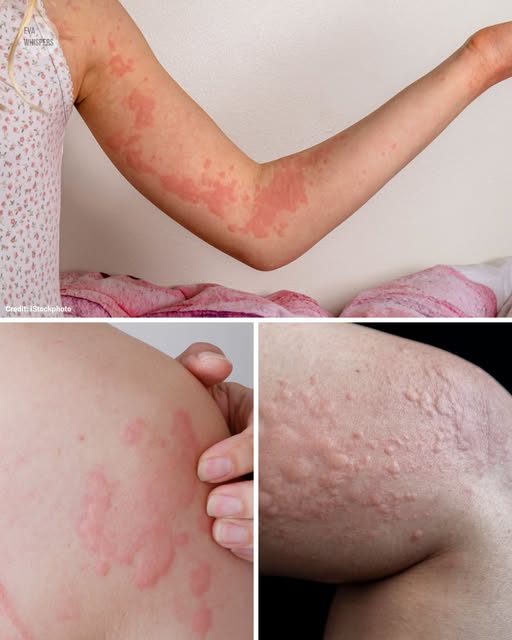
Imagine going about your day when suddenly, red, itchy patches appear on your skin. They sting, burn, and just when you think they’ve faded, they return. At first, you might blame last night’s dinner or a new detergent, but sometimes, the cause isn’t so obvious.
For many, these recurring rashes are chronic hives, medically known as chronic urticaria. While usually not dangerous, they can disrupt sleep, self-confidence, and daily life. Understanding the causes and triggers can help you manage flare-ups effectively.
What Are Hives?
Hives, or urticaria, are raised, red, itchy welts that appear when the skin reacts to inflammation. They come in two main forms:
- Acute hives: Short-lived, usually resolving within six weeks, often caused by clear allergens.
- Chronic hives: Persisting or recurring for months or even years, sometimes without an identifiable cause.
Chronic cases can be puzzling, as triggers aren’t always obvious.
Surprising Triggers Behind Chronic Hives
While food allergies are commonly blamed, hives can have many unexpected causes:
- Immune System Irregularities
Sometimes, the immune system “misfires,” releasing chemicals that inflame the skin even without a true allergen. - Hormonal Changes
Life stages such as menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can make the skin more reactive. - Stress
Emotional stress can worsen inflammation, making hives more frequent or intense. - Physical Triggers
- Heat or sweat after exercise
- Cold exposure (yes, hives can be cold-induced)
- Pressure from straps or tight clothing
- Sunlight exposure in sensitive individuals
- Viral Infections
Even a common cold or stomach bug can trigger flare-ups, sometimes appearing after recovery. - Food Sensitivities
Not just shellfish or nuts—foods high in histamine like aged cheese, red wine, or fermented products can provoke hives. - Medications
Certain antibiotics, NSAIDs like ibuprofen, and supplements can act as hidden triggers.
Warning Signs to Watch For
Monitor your skin for:
- Red, raised, intensely itchy welts
- Swelling of lips, eyelids, or face
- Shifting rashes across the body
- Flare-ups worsening at night or with activity
Seek emergency care immediately if you experience difficulty breathing or throat tightness.
Managing and Finding Relief
The good news: chronic hives are often manageable with the right approach.
Step 1: Antihistamines
Non-drowsy antihistamines are often the first and most effective line of defense.
Step 2: Prescription Options
For severe or persistent hives, doctors may recommend:
- Short-term corticosteroids
- Montelukast (commonly for asthma)
- Omalizumab (targeted injection therapy)
Step 3: Daily Lifestyle Adjustments
Small changes can make a big difference:
- Apply cold compresses for relief
- Take lukewarm baths with colloidal oatmeal
- Choose fragrance-free moisturizers
- Wear loose, breathable clothing
- Limit long, hot showers
- Practice stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing
Final Thoughts
Hives may seem simple, but they are often influenced by multiple factors: stress, hormones, infections, temperature changes, and immune system irregularities.
If chronic hives are affecting your life, remember that you’re not alone. With proper medical guidance and mindful lifestyle adjustments, you can manage symptoms and reclaim comfort. Listen to your skin—it’s giving you valuable signals.
Have you or a loved one experienced chronic hives? Share your tips and experiences below to help others find relief and understanding.