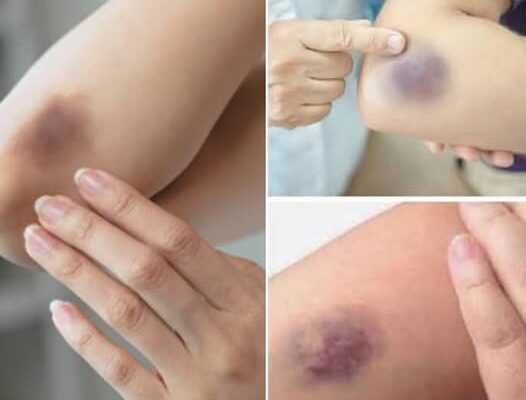
Bruising, or ecchymosis, occurs when small blood vessels under the skin break, causing blood to pool beneath the surface.
Here are some key points to know:
🟣 Common Causes of Bruising
-
Minor injury/trauma → bumping into something, sports, or falls.
-
Aging skin → thinner skin and fragile vessels make bruises more common.
-
Medications → blood thinners (like aspirin, warfarin), steroids, or even some supplements (fish oil, ginkgo).
-
Vitamin deficiencies → low vitamin C or K can increase bruising.
-
Blood disorders → like hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, or leukemia (rare, but important to rule out).
🔎 When Bruising Might Be a Warning Sign
-
Frequent, large, or unexplained bruises.
-
Bruises in unusual places (like the back, abdomen, or without any injury).
-
Bruising along with nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or prolonged bleeding from cuts.
-
Bruises that don’t heal or keep coming back in the same spot.
✅ What Helps
-
Apply a cold compress right after injury to reduce bleeding under the skin.
-
Elevate the area if possible.
-
After 48 hours, warm compresses can help improve circulation and healing.
-
Eating foods rich in vitamin C, vitamin K, and iron supports healthy blood vessels.
⚠️ If bruising is frequent, severe, or unexplained, it’s best to get checked by a doctor, since it could signal an underlying issue.
Do you want me to make y